Defects in Crystal Structure
Defects in Crystal Structure: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Schottky Defects, Frenkel Defects, Vacancy Defects, Interstitial Defects, Types of Point Defects, Point Defects and Line Defects, Impurity Defects and, Imperfections in Crystalline Solids
Important Questions on Defects in Crystal Structure
Which of the following ionic compound will show Frenkel defect?
Which of the following point defect of crystals decreases the density of a solid?
Alkali halides do not show dislocation defect because
The number of Schottky defects present in per at room temperature is
Match List I with List II
| List-I (defect) | List-II (Examples) | ||
| (A) | Frenkel defects | (1) | |
| (B) | Schottkey defects | (2) | |
| (C) | Vacancy defects | (3) | |
| (D) | Metal deficiency defects | (4) | Crystals with vacant lattice sites. |
If molten contains as impurity, crystallization can generate
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion and the other is labelled as Reason .
Assertion : In a particular point defect, an ionic solid is electrically neutral, even if few of its cations are missing from its unit cells.
Reason : In an ionic solid, Frenkel defect arises due to dislocation of cation from its lattice site to interstitial site, maintaining overall electrical neutrality.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
What are the consequences of schottky defect ?
By diffraction methods, the unit length of is observed to be . The density of is found to be . What type of defect exists in the crystal ? Calculate the percentage of and ions missing.
Give reasons: (i) In stoichiometric defects, exhibits Schottky defect and not Frenkel defect.
Examine the given defective crystal and answer the following questions:
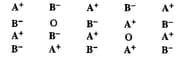
(iii) What type of ionic substance shows such defect?
Examine the given defective crystal and answer the following questions:
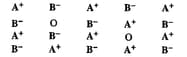
(ii) How is the density of the crystal affected by this defect?
Give reason: (i) Why is Frenkel defect found in but not in a ?
will introduce the Schottky defect if added to crystal. Explain
Why is Frenkel defect is not found in pure alkali metal halides?
Why the defects of crystalline solids are called thermodynamic defects?
What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by ?
What happens when is doped with ?
shows Frenkel defect while does not. Give reason.
ZnO turns yellow on heating. Why?
